
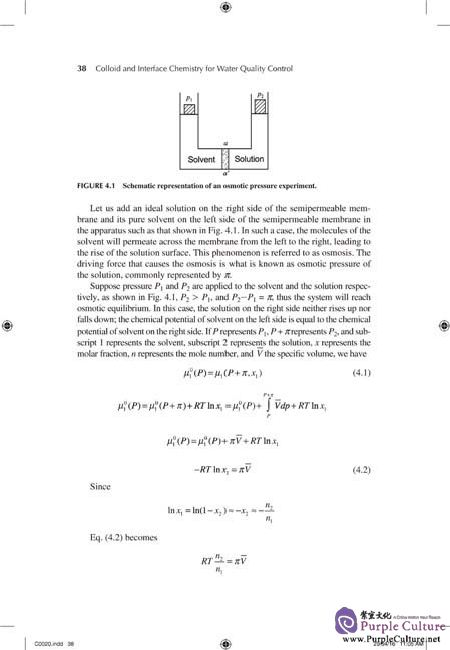




Colloid and interface chemistry is one of the most important scientifi c bases of water quality control. It is related to nearly all of the principles of water treatment,including coagulation-flocculation, sedimentation, adsorption, filtration, flotation,oil separation, membrane separation, sludge dewatering, scaling-corrosion inhibitor, and environmental atalysis. The need for water quality control has quickly increased for decades because people pay more and more attention to drinking water safety and water environment protection. Decision-making in matters relating to water quality control requires a sound understanding of basic principles of colloid and interface chemistry; therefore, the publication of this book is quite relevant at present.
This book was completed on the basis of my teaching materials in the School of Environmental and Municipal Engineering at Lanzhou Jiaotong University of China. It provides students the most basic knowledge of colloid and interface chemistry. Chapters 1–7 introduce colloid chemistry including Chapter 1 “Brief History of Colloid and Interface Chemistry and Basic Concepts,” Chapter 2 “Diffusion and Brown Motion,” Chapter 3 “Sedimentation,” Chapter 4 “Osmotic Pressure,” Chapter 5 “Optical Properties,” Chapter 6 “Rheology Properties,”Chapter 7 “Electric Properties”; Chapters 8–10 introduce interface chemistry including Chapter 8 “Surface of Liquid,” Chapter 9 “Surface of Solution,”and Chapter 10 “Surface of Solids”; Chapter 11 “Emulsion, Foam, and Gel”introduces the coarse dispersion system. As a classical science, colloid and interface chemistry has been developing for more than a century and encompasses a large amount of knowledge, but this book focuses on that which can be applied to water treatment and is closely related to the practices of water treatment and water purifi cation; therefore, students and specialists in the area will fi nd it very useful.
This book is characterized by concision, and the main basic principles and theories are introduced and described. It is easy to read and understand. I think textbooks should not be designed simply as a collection of facts but rather an introduction to ways of thinking about the world. Questions and exercises as well as their solutions have been given throughout the book so that readers can check their understanding of the text. Both traditional and some newly developed knowledge are included to refl ect the latest advances of the discipline.
I hope this book will be used as a reference book or a text book for undergraduate students and graduate students who are majoring in water quality control to help them understand the problems and diffi cult points in their studies.It could also be used as a reference for researchers and engineers as well as graduate students in other majors for further study. In addition, it is quite suitable for researchers and engineers to quickly consult relevant information that they encounter in their work because of the book’s brevity and clarity.
It is always a pleasure to thank my editor Gang Wu who has contributed so generously with illustrations and helpful suggestions to improve the book. My appreciation also goes to Dr Pengyu Liu for his work on the fi gures. Finally,I am very grateful for the fi nancial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21277065) in preparation of this book.
Qing Chang
Lanzhou Jiaotong University
Lanzhou, Gansu, China
October, 2015