Home ::
new ::
Computational Number Theory and Modern Cryptography
Details
The book is about number theory and modem cryptography. More specically, it is about computational number theory and modem public-key cryptography based on number theory. It consists of four parts. The first part, consisting of two chapters, provides some preliminaries. Chapter 1 provides some basic concepts of number theory, computation theory, computational number theory, and modem public-key cryptography based on number theory. In chapter 2, a complete introduction to some basic concepts and results in abstract algebra and elementary number theory is given.
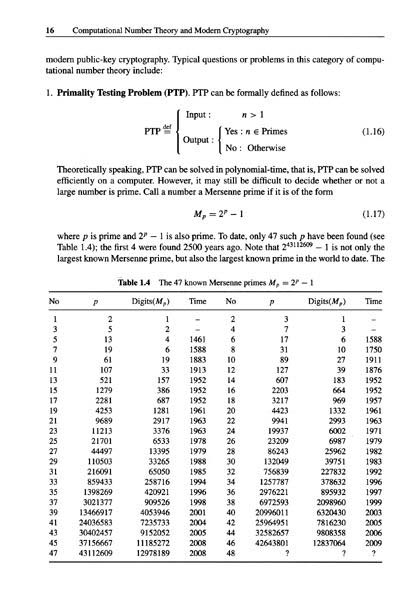
The second part is on computational number theory. There are three chapters in this part.Chapter 3 deals with algorithms for primality testing, with an emphasis on the Miller-Rabin test, the elliptic curve test, and the AKS test. Chapter 4 treats with algorithms for integer factorization, including the currently fastest factoring algorithm NFS (Number Field Sieve),and the elliptic curve factoring algorithm ECM (Elliptic Curve Method). Chapter 5 discusses various modem algorithms for discrete logarithms and for elliptic curve discrete logarithms.It is well-known now that primality testing can be done in polynomial-time on a digital computer, however, integer factorization and discrete logarithms still cannot be performed in polynomial-time. From a computational complexity point of view, primality testing is feasible (tractable, easy) on a digital computer, whereas integer factorization and discrete logarithms are infeasible (intractable, hard, difficult). Of course, no-one has yet been able to prove that the integer factorization and the discrete logarithm problems must be infeasible on a digital computer.
Building on the results in the first two parts, the third part of the book studies the modem cryptographic schemes and protocols whose security relies exactly on the infeasibility of the integer factorization and discrete logarithm problems. There are four chapters in this part.Chapter 6 presents some basic concepts and ideas of secret-key cryptography. Chapter 7 studies the integer factoring based public-key cryptography, including, among others, the most famous and widely used RSA cryptography, the Rabin cryptosystem, the probabilistic encryption and the zero-knowledge proof protocols. Chapter 8 studies the discrete logarithm based cryptography, including the DHM key-exchange protocol (the world's first public-key system), the E1Gamal cryptosystem, and the US Government's Digital Signature Standard (DSS), Chapter 9 discusses various cryptographic systems and digital signature schemes based on the infeasibility of the elliptic curve discrete logarithm problem, some of them are just the elliptic curve analogues of the ordinary public-key cryptography such as elliptic curve DHM, elliptic curve E1Gamal, elliptic curve RSA, and elliptic curve DSA/DSS.
Table of Contents
Part I preliminaries
1 introduction
1.1 what is number theory?
1.2 what is computation theory?
1.3 what is computational number theory?
1.4 what is modern cryptography?
1.5 bibliographic notes and further reading
References
2 fundamentals
2.1 basic algebraic structures
2.2 divisibility theory
2.3 arithmetic functions
2.4 congruence theory
2.5 primitive roots
2.6 elliptic curves
2.7 bibliographic notes and further reading
References
Part II computational number theory
3 primality testing
3.1 basic tests
3.2 miller-rabin test
3.3 elliptic curve tests
3.4 aks test
3.5 bibliographic notes and further reading
References
4 integer factorization
4.1 basic concepts
4.2 trial divisions factoring
4.3 p and p - 1 methods
4.4 elliptic curve method
4.5 continued fraction method
4.6 quadratic sieve
4.7 number field sieve
4.8 bibliographic notes and further reading
References
5 discrete logarithms
5.1 basic concepts
5.2 baby-step giant-step method
5.3 pohlig-hellman method
5.4 index calculus
5.5 elliptic curve discrete logarithms
5.6 bibliographic notes and further reading
References
Part III modern cryptography
6secret-key cryptography
6.1 cryptography and cryptanalysis
6.2 Classic secret-key cryptography
6.3 Modern secret-key cryptography
6.4 bibliographic notes and further reading
References
7 integer factorization based cryptography
7.1 RSA cryptography
7.2 Cryptanalysis of RSA
7.3 Rabin cryptography
7.4 Residuosity based cryptography
7.5 zero-knowledge proof
7.6 bibliographic notes and further reading
References
8 discrete logarithm based cryptography
8.1 Diffie-Hellman-Merkle key-exchange protocol
8.2 e1gamal cryptography
8.3 Massey-Omura cryptography
8.4 DLP-based digital signatures
8.5 bibliographic notes and further reading
References
……
Part IV Quantum resistant cryptography
Index